The Pacific flying squid is a fascinating species known for its unique and remarkable abilities. This fish is unique and so fasinating for so many fish enthusiast.
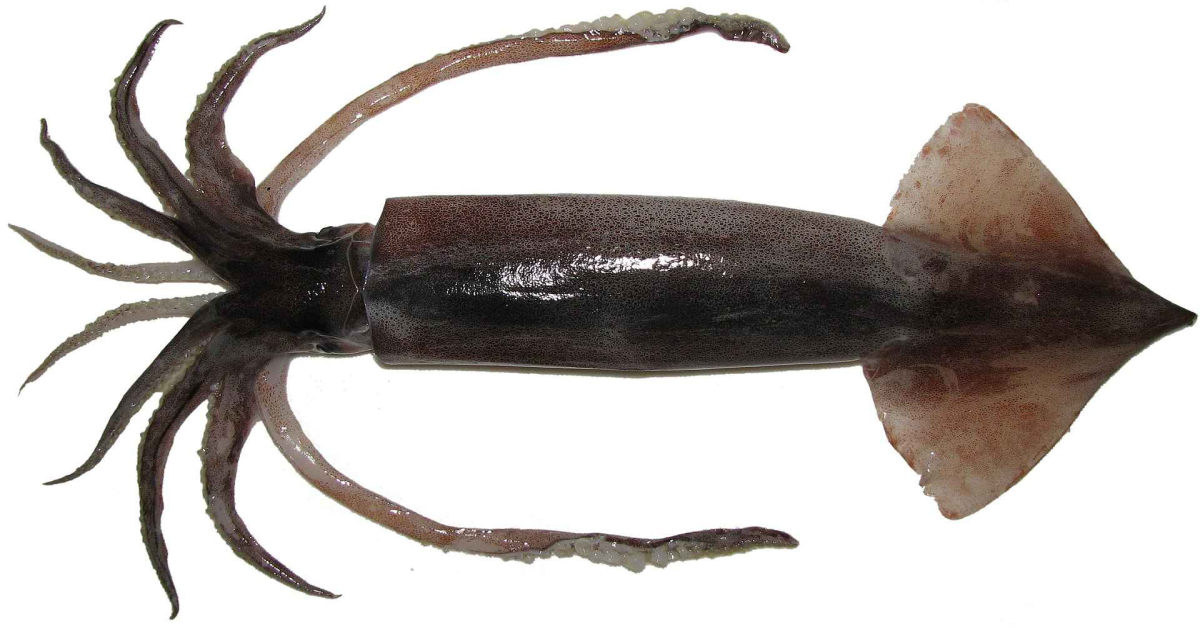
The Pacific flying squid, also known as Todarodes pacificus, is a cephalopod species found in the Pacific Ocean. These agile, carnivorous creatures have unique fin adaptations for gliding short distances above the water’s surface.
Contents
These creatures have the astonishing capability to propel themselves out of the water and glide through the air, using a technique called jet propulsion.
They can reach impressive speeds as they soar above the ocean’s surface, capturing prey with their tentacles.
We will explore how they use their jet propulsion to navigate through the waters and take flight.
We will uncover interesting facts about their habitat, including the countries where they are commonly found and the conditions they prefer.
Get ready to be amazed by the wonders of the Pacific flying squid as we dive deep into their unique abilities and unravel their secrets.
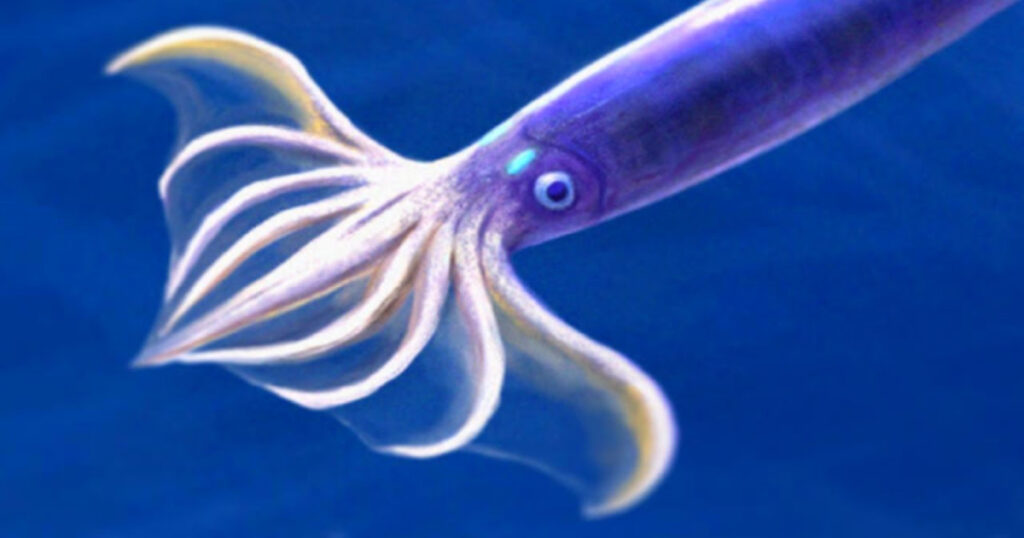
Pacific flying squid
The Pacific flying squid, scientifically known as Todarodes pacificus, is a fascinating species of squid found in the Pacific Ocean.
These adult squids are commonly seen in the central and western regions of the Pacific. They have unique characteristics that set them apart from other squids.
Distribution in the Pacific Ocean
Pacific flying squids can be found throughout the vast expanse of the Pacific Ocean. They are known to inhabit both warm and cold waters, making their distribution quite extensive.
These cephalopods are frequently observed in areas such as Japan, California, and Mexico due to favorable environmental conditions.
Why “Flying” Squids?
Despite their name, Pacific flying squids do not actually fly like birds or insects.
Instead, they exhibit a behavior called “jet propulsion,” which allows them to launch themselves out of water for short distances.
This gives them a sense of flight as they glide above the ocean surface before returning back into the water. It’s an incredible sight to witness!
Unique Characteristics
Pacific flying squids possess several distinctive features that make them stand out among other marine animals:
- Tentacles: Like all squids, they have long tentacles used for capturing prey and sensing their surroundings.
- Spherical Eggs: Females produce spherical eggs that hatch into tiny larvae called paralarvae.
- Zooplankton Diet: These squids primarily feed on zooplankton—tiny organisms floating near the ocean’s surface.
- Ink Sacs: When threatened by potential predators, they release ink from specialized ink sacs as a defense mechanism.
Ecological Importance
Pacific flying squids play a crucial role in maintaining balance within marine ecosystems:
- Predator-Prey Relationship: As predators themselves, these squids help control populations of small animals like zooplankton.
- Prey for Larger Animals: They serve as a significant food source for various marine animals, including fish, sharks, and seabirds.
Adaptations for Survival
To survive in their oceanic habitat, Pacific flying squids have developed remarkable adaptations:
- Speed and Agility: They have streamlined bodies and powerful muscles that enable them to swim swiftly.
- Camouflage: These squids can change the color and pattern of their skin to blend with their surroundings, providing effective camouflage against potential predators.
- Reproductive Strategies: Females produce a large number of eggs to increase the chances of survival for their offspring.
Unveiling the Features of Pacific flying squid
Pacific flying squid, also known as Todarodes pacificus, possess fascinating physical characteristics that set them apart from other marine creatures.
These magnificent cephalopods have streamlined bodies and an impressive size, making them highly adaptable to their oceanic environment.
Explore Their Streamlined Bodies and Impressive Size
Pacific flying squid have elongated bodies with a tapered shape, resembling torpedoes.
This streamlined design allows them to move swiftly through the water, enabling efficient hunting and escape from predators.
With an average length of 30-40 centimeters (12-16 inches), they can grow even larger under optimal conditions.
These squids also possess a unique feature called a beak. Located at the center of their tentacles, this hard structure resembles a parrot’s beak and is used for capturing prey.
The beak is incredibly sharp and strong, allowing Pacific flying squid to tear through their prey with ease.
Learn About Their Distinct Coloration and Eye Structure
One striking feature of Pacific flying squid is their distinct coloration.
They typically exhibit a reddish-brown hue on their upper body surface, while their underside is lighter in color.
This coloration helps camouflage them in the deep ocean waters where they reside.
Another remarkable aspect of these squids is their eye structure. They have large eyes that provide excellent vision in low-light conditions.
This enables them to spot prey and navigate effectively in the dark depths of the ocean.
Be Amazed by Their Uniform Size and Swimming Abilities
Unlike many other species of squid that vary significantly in size within a population, Pacific flying squid display uniformity in size among individuals.
This uniformity suggests that they all reach maturity at around the same age or size.
Pacific flying squid are highly skilled swimmers due to their muscular mantle, which propels them through the water.
They can swim at impressive speeds, reaching up to 24 kilometers per hour (15 miles per hour). This agility allows them to pursue prey and evade predators effectively.
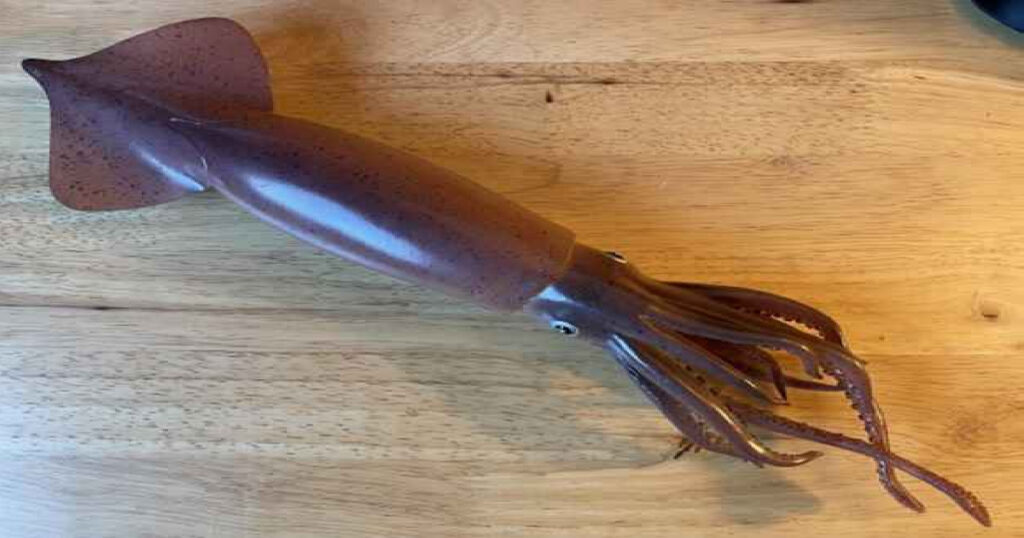

Exploring the Ocean Homes of Pacific flying squid
Pacific flying squid, also known as Todarodes pacificus, are fascinating creatures that inhabit the vast expanses of the ocean.
Let’s delve into their preferred habitats and migration patterns, as well as how they adapt to different water depths.
Discovering Preferred Habitats
Pacific flying squids can be found in various regions of the ocean, particularly along the southern coast of the United States.
These intelligent cephalopods prefer areas with abundant food sources, such as crustaceans and small fish.
They tend to congregate in large schools, making it easier for them to find sustenance and protect themselves from predators.
Migration Patterns
These squids are highly migratory creatures, constantly on the move in search of favorable conditions.
They follow surface currents that carry them across vast distances. During their migration, they traverse entire coasts and even cross open ocean areas.
Their movements are influenced by factors like water temperature and prey availability.
When temperatures drop or food becomes scarce in one area, they migrate to more favorable locations.
This ability to adapt their movements allows them to thrive in different environments.
Adapting to Different Water Depths
Pacific flying squids have evolved unique adaptations that enable them to navigate through different water depths effectively.
Their bodies possess fins that aid in propulsion and maneuverability. They have suction cups on their tentacles that help them catch prey efficiently.
In shallower waters closer to the surface, these squids rely on their fins for swift movement and use their suction cups to capture prey near the upper layers of the water column.
As they venture into deeper waters where light is limited, they rely more on their mantle muscles for propulsion while using bioluminescence as a means of communication and camouflage.
The ability of Pacific flying squids to adapt to varying water depths allows them to exploit a wide range of habitats throughout their lifecycle.
The Isolation Factor
One intriguing aspect of Pacific flying squids is their tendency to exhibit isolation behavior. This means that they often separate themselves from other squid species and form distinct communities.
This isolation can be attributed to factors such as location, water temperature, and available food sources.
By forming isolated groups, these squids can maximize the resources available to them and reduce competition for food.
It also allows them to establish a more stable social structure within their community.
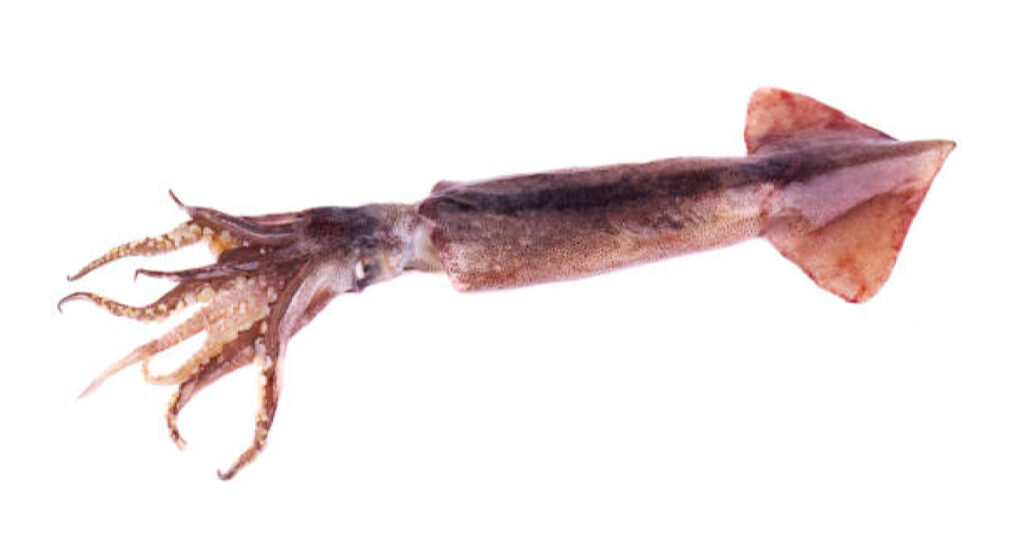

Understanding the Nutritional Choices of Pacific flying squid
Pacific flying squids are known for their voracious appetite and diverse diet.
These fascinating creatures have a wide range of food sources that they rely on to sustain themselves.
Pacific flying squids are opportunistic predators, meaning they will eat whatever is available to them in their oceanic habitat.
Their preference for small fish, crustaceans, and plankton
One of the primary food sources for Pacific flying squids is small fish. They have a particular fondness for species like anchovies, sardines, and herring.
These small fish provide an abundant source of nutrients and energy for the squids. Pacific flying squids also feed on crustaceans such as shrimp and crabs.
These crustaceans offer essential proteins and minerals necessary for their growth and survival.
Apart from small fish and crustaceans, plankton also forms a significant part of the Pacific flying squid’s diet.
Plankton consists of tiny organisms like algae, bacteria, and small animals that float in the water column.
Although plankton may seem insignificant due to its size, it serves as a vital food source for many marine creatures including the Pacific flying squid.
How they hunt and capture prey efficiently
Pacific flying squids are skilled hunters that employ various strategies to capture their prey efficiently.
When hunting smaller fish or crustaceans, these agile creatures use their powerful tentacles equipped with suction cups to snatch their prey swiftly.
They can extend their tentacles rapidly towards unsuspecting prey before ensnaring them in a tight grip.
In addition to using their tentacles, Pacific flying squids also possess sharp beaks that allow them to tear apart larger prey or break down exoskeletons of crustaceans.
This adaptation enables them to access valuable nutrients from otherwise hard-to-digest sources.
Furthermore, Pacific flying squids have the exceptional ability to propel themselves out of the water and glide through the air for short distances.
This unique behavior, known as “jetting,” allows them to escape predators and surprise their prey from above.
By utilizing this aerial advantage, they can swiftly dive back into the water and seize their unsuspecting target.
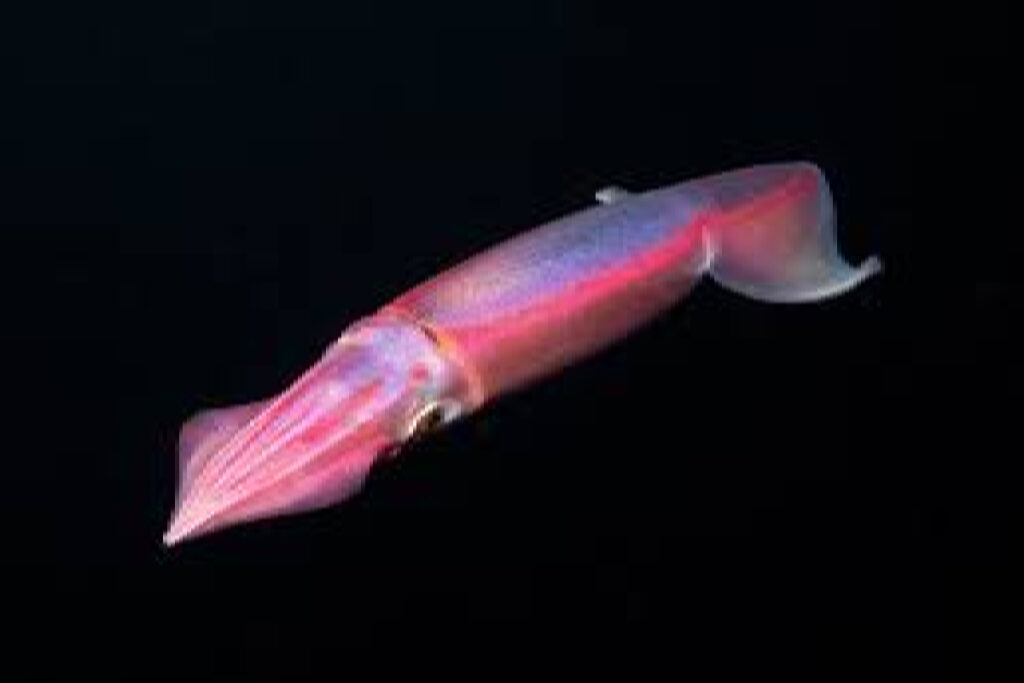

Reproduction and Life Cycle: The Journey of Flying Squid
The life history of Pacific flying squids is truly remarkable, as they go through a fascinating journey from reproduction to adulthood.
Let’s delve into the details of their mating behaviors, egg-laying strategies, and the different stages they go through in their life cycle.
Mating Behaviors and Egg-Laying Strategies
Pacific flying squids have some unique strategies up their sleeves. The males produce specialized packets called spermatophores that contain sperm.
These spermatophores are transferred to the females during mating.
Interestingly, these squids can store the sperm for an extended period until they are ready to lay eggs.
Once the female squid is ready to lay eggs, she will find a suitable location where she releases her eggs in large numbers.
These tiny eggs are laid in clusters or strings and are protected by a gelatinous substance that helps keep them together.
This strategy ensures that there is a higher chance of survival for at least some of the offspring.
The Journey from Hatching to Adulthood
After the eggs are laid, they hatch into planktonic larvae. These larvae drift along with ocean currents, feeding on small organisms like plankton until they grow larger.
During this larval stage, they undergo significant growth and development.
As these young squids continue to grow, they go through various stages known as “growth rings.”
Each ring represents a period of time when growth occurs before shedding its outer skin layer and moving on to the next stage.
This process continues until they reach adulthood.
Cannibalistic Tendencies and Migration Patterns
It may come as a surprise that cannibalism plays a role during their journey towards adulthood.
As these squids grow larger and stronger, they display cannibalistic tendencies towards smaller individuals within their own species or even other species.
Migration also plays an essential part in the life of Pacific flying squids.
They undertake long-distance migrations in search of food and suitable mating grounds.
These migrations can cover vast distances, with some individuals traveling thousands of kilometers.
Recruitment and Life in the Oceans
Recruitment refers to the process by which young squids join adult populations. Once these squids have reached adulthood, they become active members of their respective ecosystems.
Being a part of the family Ommastrephidae, they are known for their swift movements and impressive propulsion through water.
Throughout their lives, Pacific flying squids face numerous challenges, including predation from larger marine creatures such as sharks and whales.
However, they possess remarkable survival instincts that allow them to thrive in their oceanic habitats.

How Pacific flying squid Todarodes Pacificus Defies Gravity
Pacific flying squid, scientifically known as Todarodes pacificus, is a fascinating creature that possesses the extraordinary ability to “fly” through both water and air.
Unlike most squids that primarily swim using jet propulsion, these unique cephalopods have developed a specialized mechanism for aerial propulsion.
This allows them to glide above the water’s surface for short distances, defying gravity in their own peculiar way.
Pacific flying squid rely on their powerful mantle muscles to expel water forcefully from their body cavities.
By contracting these muscles rapidly and rhythmically, they create a jet of water that propels them forward with great speed and agility.
This method of locomotion is similar to how other squids swim but with an added twist.
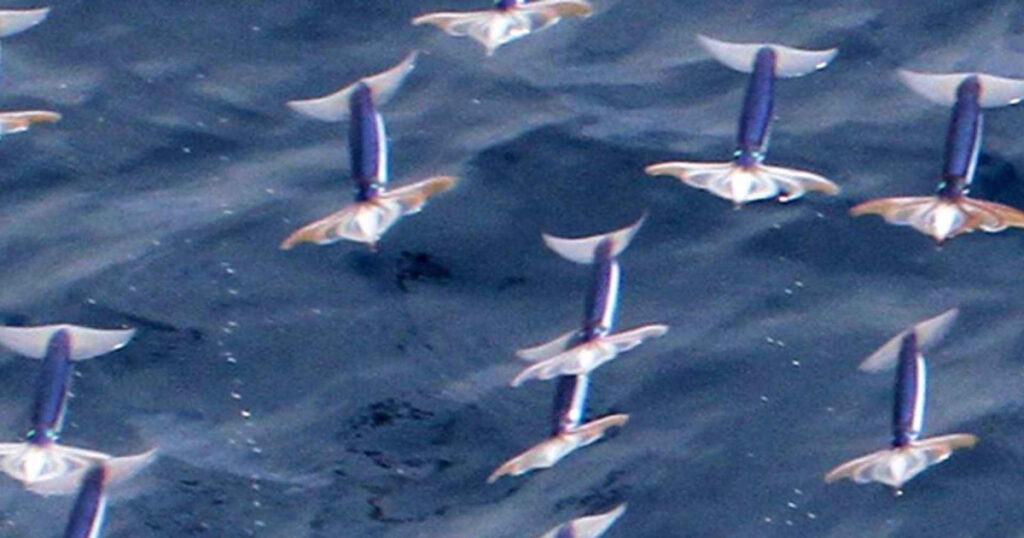
To achieve flight-like movement in the air, these squids employ a technique known as “aerial gliding.”
As they approach the water’s surface at high speeds, they extend their fins and tentacles outward.
This expanded surface area creates lift by generating aerodynamic forces similar to those experienced by birds or planes during flight.
By adjusting the angle of their fins and tentacles, Pacific flying squid can control their trajectory and maintain stability while soaring above the water.
Understand the mechanism behind their aerial propulsion technique
The aerial propulsion technique employed by Pacific flying squid involves utilizing both hydrodynamic principles underwater and aerodynamic principles in the air.
When swimming underwater, they use jet propulsion by expelling water through a funnel-shaped structure called a siphon.
The force generated from this expulsion propels them forward rapidly.
As they breach the water’s surface and transition into air, Pacific flying squid extend their fins horizontally while spreading out their tentacles like wings.
This configuration increases drag forces acting against gravity, allowing them to stay afloat and glide for short distances.
By adjusting the angle of their fins and tentacles, they can control their speed, direction, and altitude during flight.
It’s important to note that while Pacific flying squid can achieve limited flight above the water’s surface, they are not capable of sustained or prolonged aerial movement like birds or bats.
Their gliding ability is more akin to a brief leap or controlled descent rather than true flight.
Marvel at their ability to glide above water surfaces for short distances
The unique adaptation of Pacific flying squid to glide above water surfaces for short distances is truly remarkable.
This behavior serves several purposes in their lives, including predator evasion, prey capture, and even courtship displays.
By momentarily escaping the confines of the underwater world, these squids gain an advantage in pursuing prey or evading predators that may be lurking below.
This aerial maneuverability allows Pacific flying squid to expand their habitat range by exploring areas beyond what traditional swimming would permit.
It provides them with opportunities to find new food sources or locate potential mates during breeding seasons.

The Significance of Flying Squid in Fisheries
The Pacific flying squid, also known as Todarodes Pacificus, plays a vital role in fisheries worldwide.
These squids are not only fascinating creatures but also highly sought after for their culinary value.
One of the key reasons why Pacific flying squids are significant in fisheries is their abundance.
These squids have a rapid growth rate and reproduce quickly, leading to large populations.
This abundance makes them an attractive target for commercial fishing operations.
Fishermen use various methods such as gill nets to catch these squids efficiently.
The commercial fishing industry heavily relies on Pacific flying squids due to their high market value.
The meat of these squids is tender and flavorful, making it ideal for seafood dishes.
As a result, there is a constant demand for squid-based products in restaurants and supermarkets worldwide.
The abundance of flying squids can have both positive and negative effects.
On one hand, they serve as an essential food source for many marine predators such as sharks, dolphins, and seabirds.
Their presence in large numbers ensures a stable food chain within the ocean ecosystem.
On the other hand, excessive fishing of Pacific flying squid can disrupt the balance of marine ecosystems.
Overfishing can lead to a decline in their population, affecting not only those species that rely on them as prey but also other aspects of the ecosystem that depend on this delicate balance.
To mitigate potential negative impacts, sustainable fishing practices are crucial.
Governments and regulatory bodies enforce measures such as catch limits and size restrictions to ensure responsible fishing practices are followed.
By implementing these measures, it becomes possible to maintain healthy populations of Pacific flying squid while minimizing harm to the ecosystem.
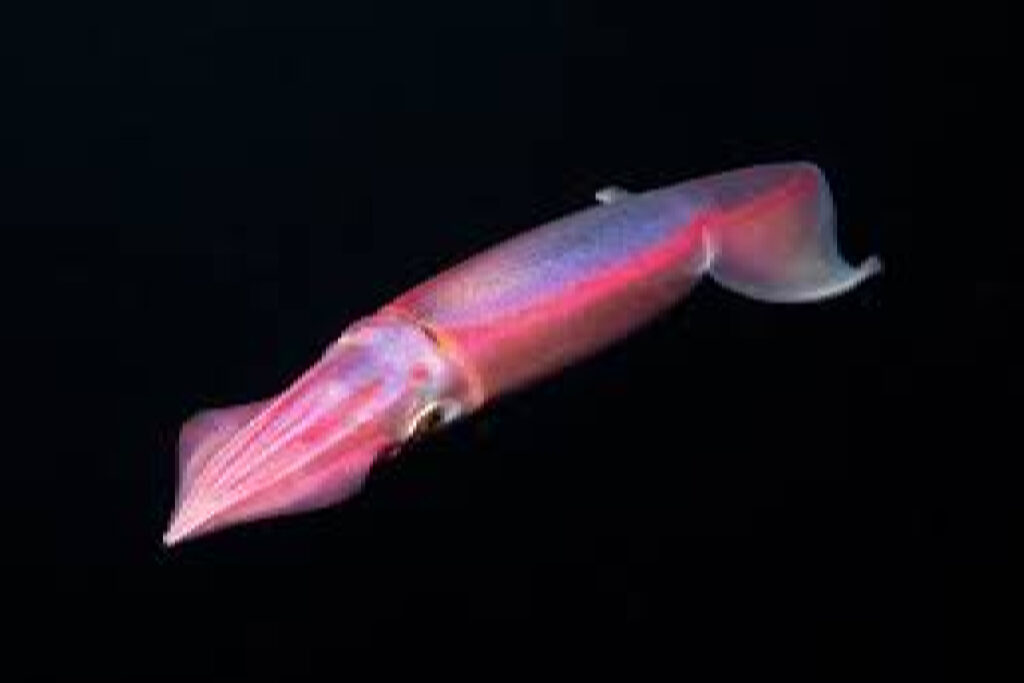

Appreciating the Wonders of Pacific Flying Squid
The Pacific flying squid is truly a marvel to behold. These unique creatures have captivated the attention of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Let’s delve into what makes them so fascinating and how they contribute to the biodiversity of our oceans.
Marvel at the beauty and uniqueness of Pacific flying squids
Pacific flying squids are known for their distinctive appearance and remarkable abilities.
They have elongated bodies that can reach up to 2 feet in length, with fins on either side that resemble wings.
These fins allow them to glide through the water with ease, earning them their name as “flying” squids.
Their iridescent skin reflects light in a dazzling display of colors, making them a sight to behold underwater.
Learn why they have become a subject of fascination for scientists and nature enthusiasts
Scientists are intrigued by the incredible adaptations of Pacific flying squids that enable them to navigate both air and water.
These squids possess specialized organs called statocysts, which help them maintain balance while soaring through the air.
They also have large eyes that aid in spotting prey from above during their aerial pursuits.
Nature enthusiasts are drawn to these creatures due to their unique hunting techniques.
Pacific flying squids are voracious predators, feeding on small fish, shrimp, and other marine organisms.
They use their eight arms lined with suckers to capture their prey swiftly.
With lightning-fast reflexes, they snatch unsuspecting victims from the water’s surface or even launch themselves out of the water to catch prey in mid-air.
Discover how these squids contribute to the biodiversity of our oceans
Pacific flying squids play an essential role in maintaining the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
As both predator and prey, they serve as a crucial link in the food chain.
By controlling populations of smaller organisms like fish and shrimp, they help regulate species abundance throughout their habitat.
Furthermore, the Pacific flying squid’s ability to fly allows them to disperse across vast distances.
Aiding in gene flow and genetic diversity within their populations.
This dispersal also contributes to the overall health and resilience of marine ecosystems.
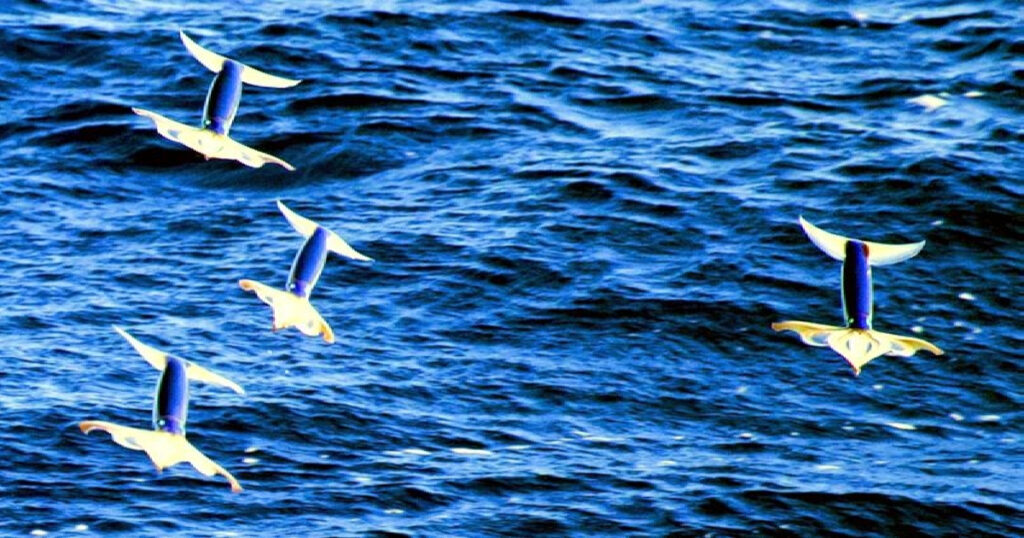

Conclusion
In this comprehensive blog post, we delved into the fascinating world of Pacific flying squid.
We unveiled their unique features, explored their ocean homes, and gained insights into their nutritional choices.
We learned about their reproduction and life cycle, as well as how they defy gravity in the vast ocean waters.
Furthermore, we discovered the significance of flying squid in fisheries and developed a deep appreciation for these remarkable creatures.
Now that you have a deeper understanding of Pacific flying squid, why not take your knowledge to new heights?
Share this information with others who might be intrigued by these extraordinary cephalopods.
Dive further into research or explore opportunities to witness them firsthand through marine expeditions or educational programs.
Let’s continue to unravel the mysteries of our oceans and appreciate the wonders they hold.
FAQs
1. Where can I find Pacific flying squid?
Pacific flying squid, also known as Todarodes pacificus, can be found in the North Pacific Ocean. They are typically found along the coasts of Japan, China, Korea, and Russia.
2. How do Pacific flying squid fly?
Despite their name, Pacific flying squid do not actually fly in the air like birds or insects. Instead, they use a unique method called “jet propulsion” to rapidly move through water using powerful siphon movements.
3. What do Pacific flying squid eat?
Pacific flying squid are carnivorous creatures that primarily feed on small fish and crustaceans such as shrimp and krill. They are opportunistic predators and have been known to consume various prey depending on availability.
4. Are there any predators of Pacific flying squid?
Yes, there are several predators that pose a threat to Pacific flying squid in their natural habitat. Some common predators include larger fish species like tuna and sharks, marine mammals such as dolphins and whales, and even seabirds.
5. Can Pacific flying squid change colors?
Yes, Pacific flying squid have the ability to change their skin color and patterns. This adaptive camouflage helps them blend into their surroundings and avoid detection by predators or potential prey.





Leave a Reply